Learn what an AI agent can do and how to begin building one in this step-by-step guide for beginners.
AI agents are the hottest topic in technology right now. But those eager to experiment face an overwhelming maze of hype, conflicting ideas, competing platforms and tricky technical and ethical challenges.
These aren’t regular chatbots.
AI agents can think, plan, take actions, and complete tasks autonomously.
A recent study by PwC suggests that AI could contribute up to $15.7 trillion to the global economy by 2030, with automation playing a key role in boosting efficiency and innovation. AI agents are central to this transformation, streamlining workflows, handling repetitive tasks, and enabling data-driven decision-making. From virtual assistants in customer service to intelligent fraud detection in finance, these agents are reshaping industries and driving business growth.
What Are AI Agents?
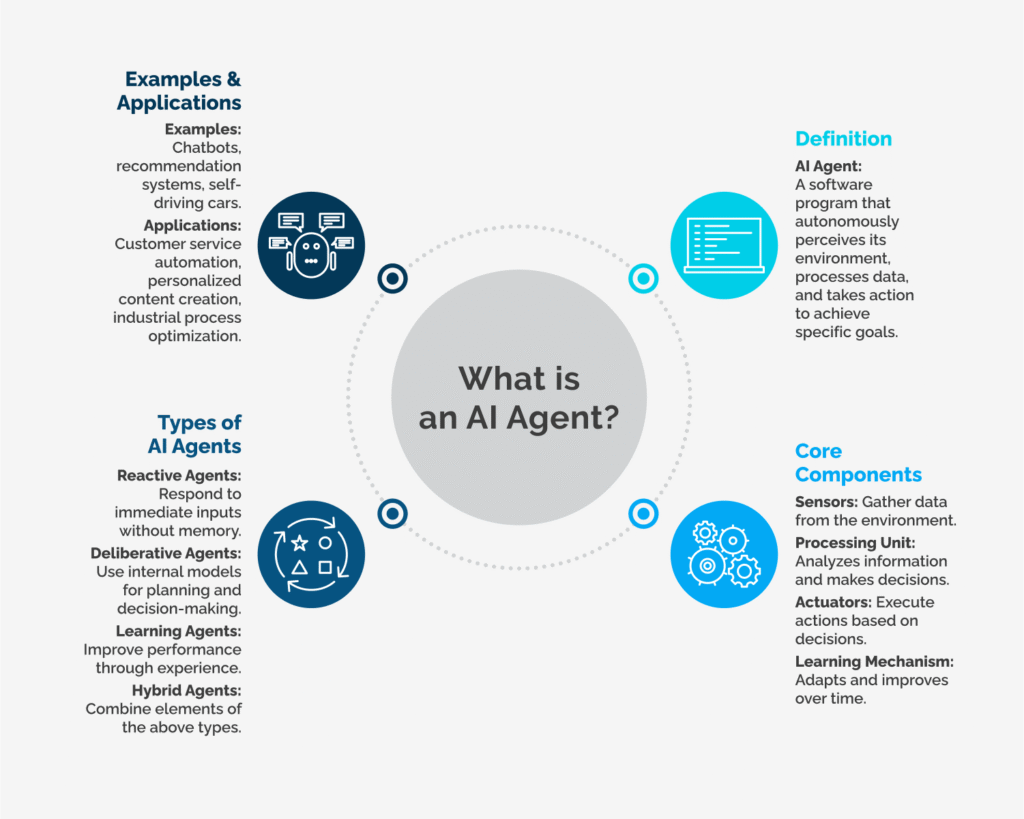
An AI agent is a system that:
✅ Understands instructions
✅ Makes decisions
✅ Uses tools or APIs
✅ Performs tasks automatically
✅ Learns from feedback over time
Think of it as your digital employee who doesn’t sleep, doesn’t get tired, and can run 24/7.
🌍 Related: WhatsApp’s Massive Privacy Upgrade 2025 — Use Username Instead of Number Sharing
Examples include:
- Social media automation agents
- Research or data-analysis agents
- Customer service agents
- Sales outreach agents
- Coding and debugging agents
- Personal productivity assistants
Types of AI Agents
1. Reactive Agents
- Description: Respond immediately to inputs without storing past interactions.
- Example: Chess-playing bots that make decisions based solely on the current board state.
2. Deliberative Agents
- Description: Use internal models and planning strategies to make more informed decisions.
- Example: Autonomous delivery robots that plan optimal routes.
3. Learning Agents
- Description: Improve their performance over time using machine learning techniques.
- Example: Netflix’s recommendation engine that evolves with viewer behavior.
4. Hybrid Agents
- Description: Combine elements of reactive and deliberative systems for more robust performance.
- Example: Smart home systems that both react to immediate stimuli and plan for future energy efficiency.
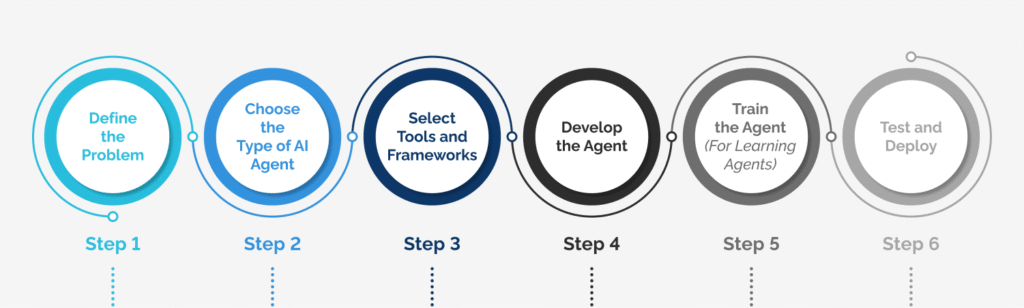
How to Build an AI Agent: 8 Steps
Here’s a structured approach to creating an AI agent:
- Define the Objectives and Use Case
Before developing an AI agent, it is important to determine the problem it will solve (e.g., customer support, data analysis, automation) as well as to identify its inputs (sensors, text, images) and desired outputs (responses, actions). A few examples of the use-cases can be:
- Customer Support: AI chatbots that provide instant responses to customer queries, reducing the need for human intervention.
- Process Automation: Automating repetitive tasks such as data entry, document processing, and transaction verification.
- Predictive Analytics: Using AI to identify trends, detect anomalies, and make informed business decisions based on historical data.
- Autonomous Systems: AI-powered robots and self-driving cars that operate with minimal human input.
- Choose the Right AI Model
AI agents rely on different types of models. The approach you select depends on your agent’s complexity and learning requirements. Below is list of models that can be used:
- Rule-Based Systems: If-then logic for simple tasks, such as automated email filtering or spam detection.
- Machine Learning Models: Use statistical techniques to learn from historical data, improving decision-making over time.
- Deep Learning Networks: Neural networks designed for complex tasks like speech recognition, image classification, and sentiment analysis.
- Reinforcement Learning Models: Allow AI agents to learn through trial and error, optimizing performance in areas like robotics and gaming.
- Collect and Prepare Data
AI agents require quality data for training as proper cleaning and labeling can make or break your agent’s performance. The data preparation process includes several key steps.
- Data Collection: Gathering structured data (databases, spreadsheets) and unstructured data (text, images, videos).
- Data Cleaning: Removing duplicates, handling missing values, and standardizing data formats to ensure consistency.
- Data Annotation: Labeling data where necessary, such as categorizing customer service inquiries for training chatbots.
- Data Splitting: Dividing data into training, validation, and testing sets to evaluate the AI model’s performance.
- Develop the Core Logic and Algorithms
Choosing the right algorithm depends on the AI agent’s purpose.
- Supervised Learning: Requires labeled data for training (e.g., classifying emails as spam or not spam).
- Unsupervised Learning: Identifies patterns in data without labels (e.g., customer segmentation in marketing).
- Reinforcement Learning: Trains the AI agent through rewards and penalties (e.g., game-playing AI that learns strategies over time).
- Train and Evaluate the Model
Training transforms raw data into intelligence. Be patient – good models take time to develop. Use frameworks like TensorFlow, PyTorch, or Scikit-learn to train the AI model. The following steps should be taken to get a well-trained model.
- Training the Model: Feeding it data and allowing it to adjust its parameters based on error minimization.
- Hyperparameter Tuning: Adjusting variables like learning rate and batch size to optimize performance.
- Performance Metrics: Measuring accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score to assess how well the AI agent functions.
- Validation Testing: Running the AI agent on unseen data to ensure it generalizes well.
- Integrate with APIs and Tools
To enable real-world interactions, connect the AI agent to APIs such as:
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): OpenAI’s GPT, Google’s BERT for language understanding.
- Computer Vision: OpenCV, TensorFlow Vision API for image recognition.
- Speech Processing: Google Speech-to-Text, IBM Watson for voice recognition and synthesis.
- Database Connectivity: MySQL, MongoDB, PostgreSQL for storing and retrieving information.
- Deploy the AI Agent
Choose a deployment method based on the use case.
- Cloud-Based Deployment: Services like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud provide scalable infrastructure for AI workloads.
- On-Premises Deployment: Suitable for industries with strict data security requirements, such as finance and healthcare.
- Edge Deployment: Allows AI agents to run on local devices like IoT sensors, reducing latency for real-time applications.
- Containerization: Using Docker and Kubernetes to manage AI applications efficiently across different environments.
- Monitor and Optimize
After deployment, continuously monitor the AI agent’s performance.
- Performance Logging: Tracking system responses, processing times, and user interactions.
- Error Analysis: Identifying incorrect predictions and refining the model based on new data.
- Periodic Model Retraining: Updating the AI model to adapt to evolving trends and requirements.
- Security Audits: Preventing adversarial attacks that could manipulate the AI agent’s behavior.

How AI Agents Work (Simple Breakdown)
Most AI agents have 4 basic components:
1. The Brain (LLM)
This is usually models like GPT-5, Claude, Llama, Gemini, etc. It handles understanding and reasoning.
2. Memory
Agents need short-term memory to track a task and long-term memory to store results or user preferences.
3. Tools
These could be:
👉 Web browsing
👉 APIs
👉 Databases
👉 Automation tools (Zapier, Make, AirOps, etc.)
👉 Code execution
Tools allow the agent to *act*, not just talk.
4. Environment
Where the agent performs tasks—this could be your laptop, a cloud server, or a hosted agent platform.
Ideas for Simple Agents You Can Build Today
Here are some beginner-friendly ideas:
- Content repurposing agent(turns one video into 10 posts)
- SEO research agent
- Social media scheduler agent
- Data entry & cleaning agent
- PDF summarizer agent
- Affiliate marketing automation agent
- Customer query reply agent
- Amazon/Shopify product research bot
Why AI Agents Are the Future
AI agents are becoming the backbone of:
- E-commerce
- Content creation
- Marketing
- Software development
- Customer support
- Education
- Personal productivity
Soon, every business—big or small—will use them.
And creators who learn to build agents now will have a massive advantage in 2026 and beyond.
💡 Read next: OpenAI Sora 2 Capabilities & Real-World Uses Explained
Final Thoughts
Building an AI agent is no longer something only developers can do. With modern agent frameworks and powerful models, anyone can create an AI assistant that automates real-world tasks.
Start simple, experiment, and keep improving.
Your first agent may not be perfect—but it might be the beginning of something powerful.
📸 Stay Updated!
Follow us on Instagram for the latest business, world news & tech trends.
➜ Follow @FasturiousOfficial