Deep Fake Detection is no longer just a research topic—it’s an urgent necessity. Deepfakes aren’t just a technological curiosity; they’re a fast-evolving threat with real-world consequences. The advancement of artificial intelligence has made it easier than ever to create convincing false content, fueling misinformation and disinformation in modern society.
What is a Deepfake?
A deepfake is synthetic media—most commonly a video, audio clip, or image—generated or manipulated using artificial intelligence to appear convincingly real.
The word “deepfake” comes from a blend of deep learning and fake, pointing directly to the technology behind it.
Common deepfake types include:
- Face swaps
- Lip-sync deepfakes
- Voice cloning
Learn more about how AI shapes synthetic content in our Technology section
How Are Deepfakes Made?
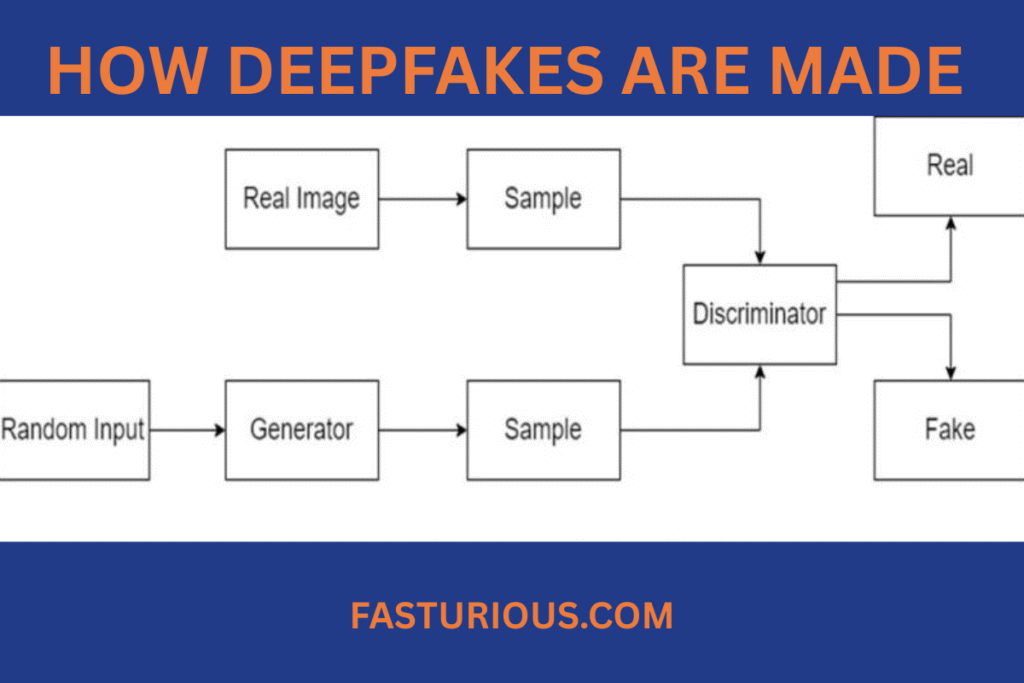
Deepfake creation relies on two AI systems working together:
- The Generator – creates fake content (faces, voices, etc.).
- The Discriminator – evaluates if the content looks or sounds real.
Through thousands of iterations, the generator improves until its synthetic media becomes nearly indistinguishable from reality.
🔍 Unfortunately, these tools can be exploited for financial fraud, identity theft, and political misinformation (MIT Media Lab study).
Red Flags: Signs of a Deepfake
- Facial movement anomalies: Misaligned eyes, distorted teeth, or unnatural blinking.
- Lighting inconsistencies: Shadows that don’t match the environment.
- Lip-sync mismatches: Audio doesn’t align with mouth movements.
- Background noise anomalies: Static, echo, or distortion in voice cloning.
- Too perfect or strange: If something feels “off,” trust your instincts.
Techniques for Verification (Manual Checks)
Even without advanced tools, you can manually verify authenticity:
- 🔍 Reverse Image Search – via Google Images or TinEye.
- 📰 Cross-check sources – verify if the clip exists on reliable news outlets.
- 🗂 Analyze metadata – check file creation details.
- 🎥 Compare with known media – review older clips of public figures for mannerism consistency.
For cybersecurity enthusiasts, we cover more hands-on guides in our Cybersecurity category.

Where Are Deepfakes Commonly Used?
| Use Case | Impact |
|---|---|
| Fake news & misinformation | Propaganda & manipulation of public opinion |
| Scams & identity theft | Voice cloning for CEO fraud & phishing scams |
| Deepfake pornography | Non-consensual content targeting women |
| Bypassing authentication | Tricking facial/voice recognition systems |
According to Europol’s cybercrime report, deepfakes are increasingly linked to organized digital crime.
Tools for Deep Fake Detection
Here are some effective detection tools available in 2025:
- Deepware Scanner – Detects manipulated videos.
- Microsoft Video Authenticator – Evaluates stills and videos for deepfake probability.
- Reality Defender (RD) – Real-time deepfake detection as a browser extension.
- Deeptrace – Professional-grade deepfake monitoring platform.
- InVID (browser plugin) – Widely used by journalists to verify news images & videos.
For an in-depth tool comparison, see this Wired deepfake detection guide.
Final Thoughts
Deepfakes represent a double-edged sword: groundbreaking technology with dangerous applications. That’s why Deep Fake Detection is now more critical than ever.
- Individuals should learn how to spot fakes.
- Organizations must invest in detection tools.
- Governments and tech leaders need regulation.
So next time you come across a video that feels “too good to be true” — pause and ask: Is it real — or is it a deepfake?
Expert Insights
“The capabilities of generative AI models are improving at an exponential pace. Within months—or at most a few years—even experienced users will find it challenging to recognize AI-generated content. We should prepare with both technology and regulation.”
— Juraj Jánošík, Director of AI
1 comment
[…] 📌 Related: Deep Fake Detection: Tools & Techniques That Actually Work in 2025 […]